Types of Skin Cancer
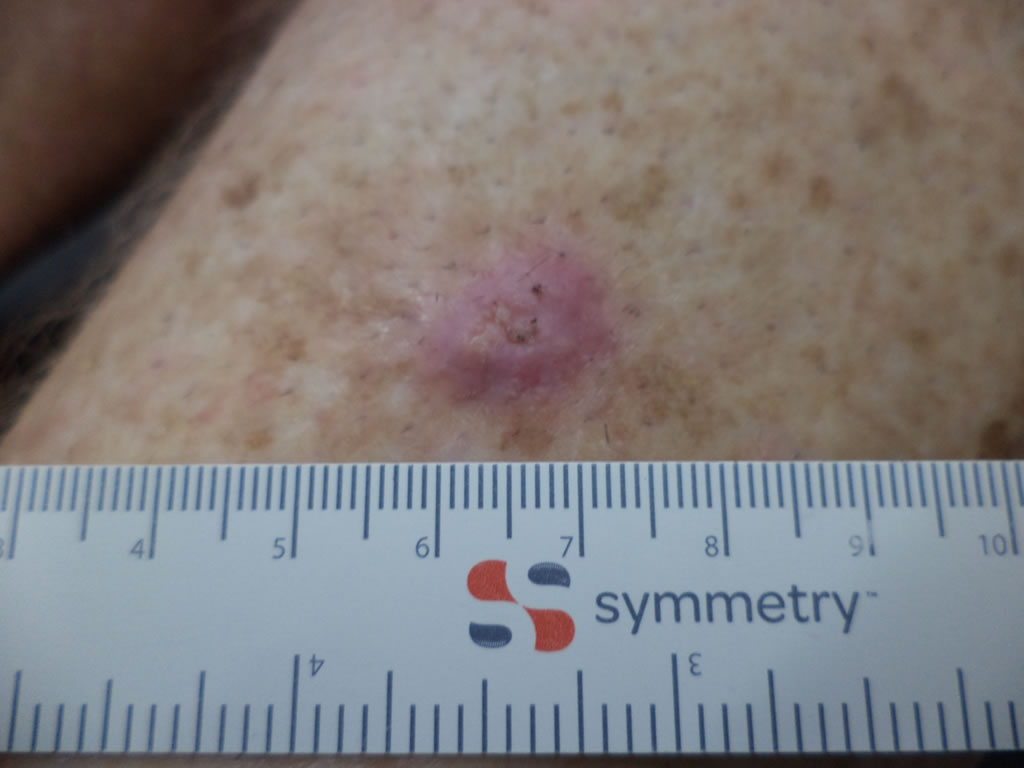
Basal Cell Carcinoma ( BCC )
- BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and the least dangerous.
- They result from UV radiation exposure and occur on sun exposed areas.
- They are rarely life threatening, but can become very problematic if not treated
- Most require surgical excision, some superficial types may be suitable for cream or curettage treatment.
- Advanced cases may also need radiation therapy.
- There are several types of BCC with varying appearance. Some are pearly lumps, while others are red and flat or subtle scar like infiltrating lesions.
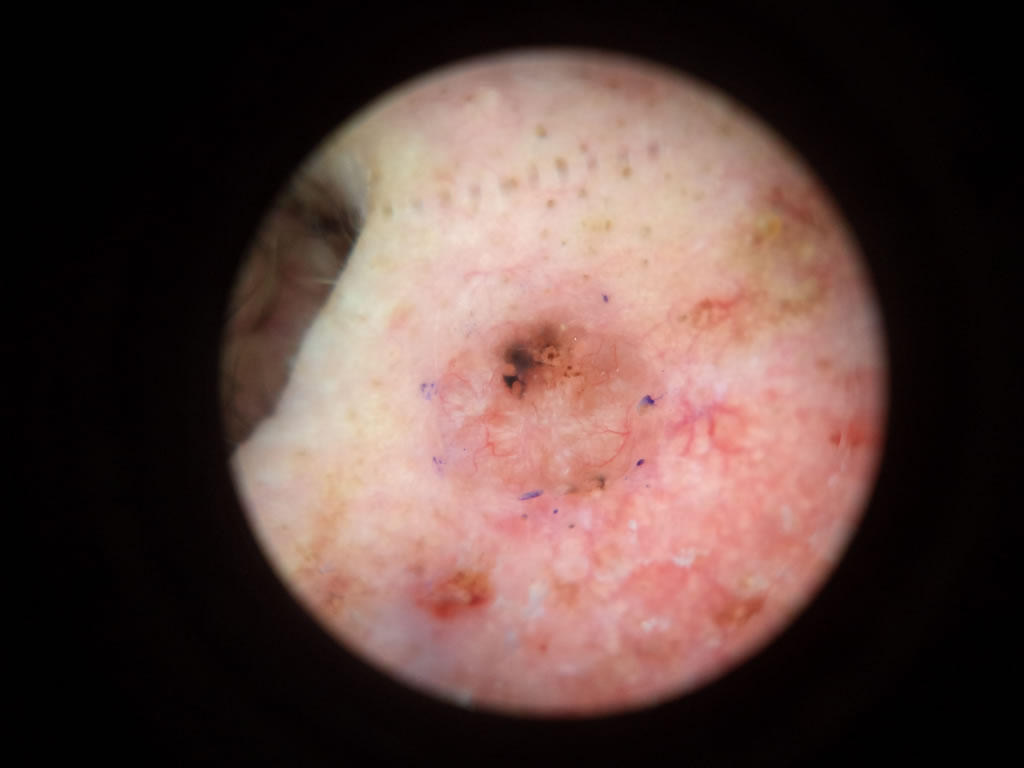
Squamous Cell Carcinoma ( SCC )
- SCC are mostly caused by excessive UV radiation exposure.
- They can be aggressive and spread to other parts of your body if left untreated. It is estimated that about 500 Australians die from skin SCC each year.
- All invasive SCC require surgical excision where possible. Precursor lesions ( solar keratosis/ Bowens disease) can be removed either surgically, with creams or cryotherapy, depending upon the size and site of the lesions.
- Advanced cases may also need radiation therapy.
- They begin as red scaly lesions that grow and often become tender.
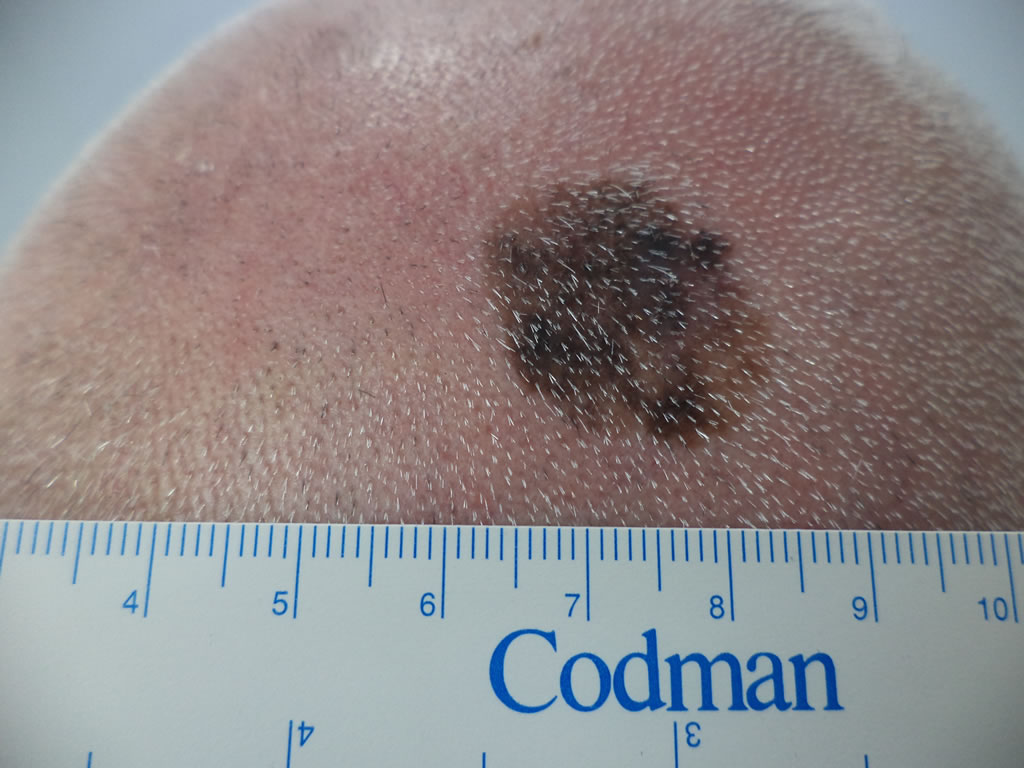
Melanoma
- Approximately 1500 Australians die every year from melanoma. Melanoma is the 4th most common cancer in Australia
- 1 in 14 men and 1 in 23 women develop melanoma in their lifetime
- Early detection gives the best chance of cure
- Melanomas mostly develop in high sun exposed skin, but can occur on skin not exposed to the sun and in rarer cases, at the back of the eye or gastrointestinal tract.
- Melanomas can arise in pre-existing moles, but more commonly develop as new spots in normal looking skin
- They can be brown, black, pink, grey, blue or even skin coloured
- The hallmark of melanoma is change in colour, size and shape over weeks or months
- Early presentation to a doctor for any changing spot and regular full skin checks are the best way to detect melanoma early
- Surgical treatment is required for melanomas
- Surgical treatment involves excision of the lesion initially, often followed by a second wider excision once the result is received. Primarily, the thickness of the melanoma determines the further treatment needed. Some cases need specialist referral and lymph node sampling.
- People who have had melanoma are at higher risk of getting more melanomas. Other risk factors include: fair skin, high UV exposure, many moles, melanoma in 1st degree relative and increasing age.
- Regular skin checks every 3-6 months are advised for anyone who has been diagnosed with melanoma